Disclaimer: Any views expressed in the below text are the personal views of the author/s and do not constitute investment advice or recommendations for investments. The author/s views should not form the basis for making investment decisions - invest in markets at your own risk after performing thorough due diligence.
In the last post, we explored the events surrounding the implosion of the LUNA/UST ecosystem and drew many parallels with that of the Lehman collapse of 2008. We concluded that an event of this magnitude within a quickly evolving ecosystem and new asset class would lead to overall positive outcomes in increased accountability, due diligence and experience for new protocols and investors alike.
A short terminology lesson is needed before we get into the wall of text below. We use the term ‘goblin’, or synonyms thereafter, to allude to something terrible or distressing. It is a term commonly used by crypto natives who have spawned an entire lexicon of terminology after many years of combined trauma and euphoria. The vocabulary and phraseology have been honed over the past decade to communicate the experience of riding on the emotional rollercoaster that is the market.
Setting The Scene
Summer 2020 saw DeFi explode into the blockchain space, demonstrating the first major use case of a technology that had arguably been solely used for speculation up until that point. With the launch of Uniswap V2 on Mainnet in May 2020, the COVID liquidity crisis and the subsequent QE/helicopter money flowing into the space, a new era of opportunity had begun.
In its simplest form, DeFi, or Decentralized Finance, uses smart contracts to automate financial interactions between market participants. This simultaneously removes the need for intermediaries and increases financial inclusivity. DeFi provides a variety of investment opportunities to all market participants - not just an exclusive cabal. These opportunities are delivered through several novel financial products. These products are available through a variety of DApps.
Through these DApps, market behaviours that have been the strict purview of larger financial institutions are now accessible to the average retail investor. These behaviours include the ability to profit from liquidity provision, loaning of assets and derivatives trading; whether this is a good thing we will cover in subsequent articles.
This week we are exploring the notion of whether DeFi is dead. A violent few months in the market and a severe lack of utility, sustainable long-term yields and economic models have caused significant worry for many as most protocols have been slowly bleeding out. This bleed out has served as a beacon for the most loathed market participant of them all: the goblin. These factors have coalesced to provide the ideal conditions for goblin settlers from far and wide. DeFi is currently a goblin garden of Eden – we all know how much they like to short overvalued assets.
The Risk Curve - Hedger Or Degenerate
An important concept to understand before we go further is the risk curve. Modern Portfolio Theory uses the risk curve to display the potential benefits of different portfolios across the efficient frontier. Portfolios that lie below the curve or efficient frontier are sub-optimal - based on historical returns, they do not provide enough return for the level of risk assumed. These assets provide investors with a higher return on investment to compensate them for the excess risk taken. We will delve into further depth on this in future articles.
In the context of crypto, BTC and ETH spot assets, or ETH/USDC LP tokens, would be found towards the left of the curve. The coin your favourite influencer posted about last week, or any LP token for said asset would be so far off the right of the curve that you should probably partake in several hours of Wim Hof method breathing whilst reevaluating all the “investments” you have ever made. You should then consort with the goblin council for guidance on repenting.
Figure 1 - Efficient frontier risk curve demonstrating portfolio construction in regards to ratio between % return and % risk. Source: Investopedia
Surveying The Goblin Battlefield
A common metric for quickly summarising the relative value of a DeFi protocol is to examine the TVL or total value locked. The TVL is the sum of all staked assets earning rewards and interest. Larger flows can also dictate retail and institutional sentiment for that particular protocol.
The below image depicting the highest market cap protocols shows how value has been annihilated over the last month due to the broader risk-off stance in global markets. The goblins have been feasting, but aren’t quite done yet.
Figure 2 - TVL across top L1s. Source: DeFi Llama
Briefly scanning the carnage above, we see that AVAX and FTM have been hit the hardest in the recent value purge, whilst WAVES and TRX are holding firm.
TRX's strength in this sector is attributable primarily to the recent issuance of USDD by the TRON DAO Reserve. USDD is a cryptocurrency issued by the TRON DAO Reserve. It will have a built-in incentive mechanism and a responsive monetary policy, thus allowing USDD to stabilise against any price fluctuations and help consolidate the value of USDD as a true settlement currency. A decentralised currency protocol with a stable price will significantly expand the use cases for cryptocurrency – if successful. In the wake of LUNA/UST (which we provided a post mortem of here) and the recent issues with algorithmic stablecoins, the success of USDD remains to be seen.
Next, we can see the FTX DeFi Index chart below. The value of this index is calculated from the weighted average of the assets listed on the chart itself. As with our earlier observations on the goblin-induced TVL haemorrhaging, the bleed has been brutal and continuous from November 2021 until now, with but a moment of brief respite in March 2022.
When charting, we like to keep things extremely simple. Simplicity is critical when reading price action as one can quickly become overwhelmed by the data available. The red horizontal support represents our ‘goblintown line’ (bad things tend to happen if this is crossed), whilst the blue represents a key pivot region. We will delve into more depth on this in further articles. Our methodology is applicable across all markets and asset classes.
Figure 3 - FTX DeFi Index, an aggregated basket of the listed assets. Source: Tradingview
In response to the above, there has been a concerted flight to safety toward USDC and DAI stablecoins. As a result, supply-side yields in these assets have collapsed to <2% in most cases. The only platforms still offering the yields of the pre-goblin era are paying those yields in a useless farming token with zero utility or economic value.
To the left of the DeFi risk curve, we see a collapse in yields offered. The active and popular ETH/USDC pair on Uniswap V3 is projected to pay around 12%. This is with the very present risk of impermanent loss, a common factor many yield farmers need to account for when extracting yield from a risk asset/stablecoin pair.
Whilst the recent LUNA/UST failure was due to mismanagement, hubris and issues inherent to algorithmic stablecoins, it is far from the only failure. There have been numerous other DeFi hacks and exploits in the past 12 months. They have been swift, targeted and eviscerated investor capital with brutal efficiency. A key point here is that these hacks happened during a bull market and survivability tends to be better. Protocols are more robust during a bull run due to increased cash flow provided by the willing exit liquidity of the average retail investor. Marketing can be unimaginative and content can lack creativity, but this doesn’t matter because a losing horse will always be backed by endless hordes seeking the next 100x.
We have found through our research that this concept is completely inverted during a period of bearish market activity. The reasons for this are many but tend to revolve around issues with cash flow. Due to the space's open nature and the relative accessibility of development, protocol and project teams tend to overlook responsible treasury management. This could be due to oversight, a lack of experience, or bull-market-induced-euphoria. It manifests as misallocation, mismanagement and even misappropriation of funds. When times are lean and retail investors are nursing the wounds dealt by the goblin legions, the average project can be hamstrung by issues they would have easily overcome with different market conditions. The survivability of hacks is much lower and the previously deep wells of unearned trust tend to run dry far quicker.
This represents a boon for the DeFi developers, builders and protocols that have been sustainably constructed and operated. Effective project and risk management now begin to shine through, allowing these projects to carve out their respective niches. Conversely, weak and vulnerable protocols with nothing more than bull market euphoria will succumb to the goblins. Armour of empty promises, shields of zero experience and swords of minimal credibility count for nothing in the face of the goblin menace. This cohort is actively losing the war with the goblin army.
Defi Hacks and Protocol Vulnerabilities
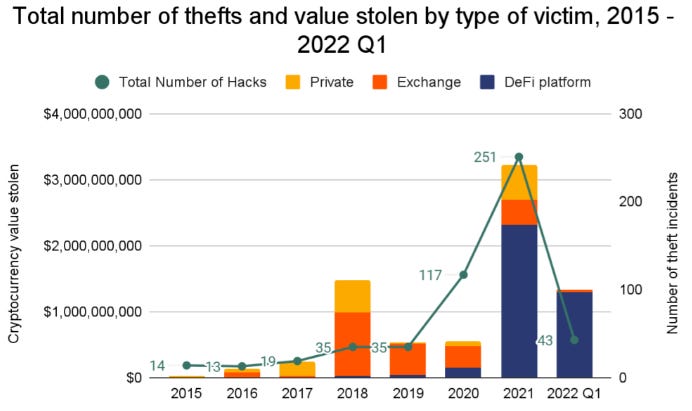
Chainalysis research has recently found that almost 97% of all cryptocurrency stolen in the first three months of 2022 has been from DeFi protocols, this is significantly up from 72% in 2021 and 30% in 2020. The trend is worrying to say the least.
Figure 4 - Total number of thefts and value stolen sorted by victim type. Source: Chainalysis
Historically, hacks have primarily been the result of security breaches in which hackers gained access to victims’ private keys through user mismanagement or phishing. The Ronin Network March 2022 breach, which enabled the theft of $615 million in cryptocurrency, has proven the continued effectiveness of these techniques.
Figure 5- Top 10 cryptocurrency theft incidents. Source: Chainalysis
Hacks to DeFi protocols are generally the result of faulty code. Automation of protocols through smart contracts, though more efficient, does introduce more risk and another potential attack vector. Code exploits and flash loan attacks have accounted for much of the value stolen outside of the Ronin attack. Code exploits occur for many reasons, with the core DeFi tenets of decentralisation and transparency being major contributing factors. The miners and validators on a permissionless blockchain cannot deterministically verify all external inputs. Therefore, they will allow the execution of anything that matches the predefined criteria of the smart contract.
Open-source development is central to the ethos of DeFi. As DeFi protocols move funds autonomously, users should be able to audit the base code to verify that the protocol is functioning correctly. However, this benefits cybercriminals who can also analyse the base code for vulnerabilities and attack vectors in many instances.
Alternatively, flash loan attacks are sometimes caused by DeFi platforms’ reliance on unstable price oracles. Oracles are tasked with maintaining accurate pricing data for all cryptocurrencies on a platform. Fast yet insecure oracles are vulnerable to price manipulation, whilst slower and more secure oracles are susceptible to price arbitrage. Fast yet insecure oracles often provide vectors for flash loan attacks, which extracted a massive $364 million from DeFi platforms in 2021. For example, in the hack of Cream Finance in October 2021, a series of flash loans exploiting a vulnerability in the way Cream calculated yUSD’s “price per share” variable enabled attackers to inflate yUSD price to double its actual value, sell their tokens and bank $130 million in a 4-hour window.
Code exploits and price oracle inaccuracy are routinely used as attack vectors, underscoring the need for increased security and accountability in DeFi protocols.
As the space grows and evolves, solutions are being developed to combat the above scenarios. To ensure pricing accuracy, decentralised price oracles such as Chainlink or Witnet can protect platforms against price manipulation attacks. To ensure smart contract security, code audits can protect programs against common hacks like unhandled exceptions, reentrancy and transaction order dependency.
DeFi is not dying, instead it is going through a natural evolutionary phase of extreme growing pains.
Ponzinomics 101: How do DeFi Protocols Generate Revenue?
To assess the current health of the DeFi ecosystem, it is necessary to look under the hood of what is driving the main value proposal - the yields. Two main factors drive yields:
Demand for leverage
Fee generation through network transactions
Retail demand for leverage is cyclical yet highly correlated with price action in the markets. Retail traders seek to add leverage to positions during risk-on bullish market phases, thereby capturing better risk:reward payoffs. We can see in the below image that many traders have been liquidated both on the long and short side of the book during the recent moves and market volatility.
Figure 6 - ETH total liquidations during March 2022. Source: Coinglass
The more accurate indicator of retail demand for leverage is the funding rate of perpetual futures products, which remains elevated. After analysing historical rates, we can see that there is still considerable demand to remain exposed to short and long leverage on assets such as ETH and BTC.
Figure 7 - ETH perp funding rates during May 2022. Source: Skew
Meanwhile, a steady demand continuously pours in from ‘smart-money’ investors looking for leverage to apply various market/delta neutral strategies. A common hedge fund trade we have participated in many times is to buy/long ETH spot whilst simultaneously selling/shorting futures (only if the price in futures is higher than spot) - thereby profiting from holding the ETH exposure to expiry in a near risk-free manner. This is known as a ‘contango’ trade, whilst the spread is known as the ‘basis’. It reflects broader institutional investor interest in the ecosystem - contango has been present lately but can disappear at any given moment.
The DeFi space doesn’t look too bleak from the network fee generation perspective. Below we can see the CRV fees generated during the LUNA/UST crash and the in-flow of extremely anomalous volumes. This particular protocol has shown that value capture during periods of extreme market volatility is extremely beneficial to the token holder and is an example of a ‘productive’ asset in DeFi. We will go into more depth on CRV later in this article.
Figure 8 - Weekly fees generated by the Curve protocol. Source: Curve Protocol
Figure 9 - Total revenue generated overlaid over fully diluted mcap. Source: Token Terminal
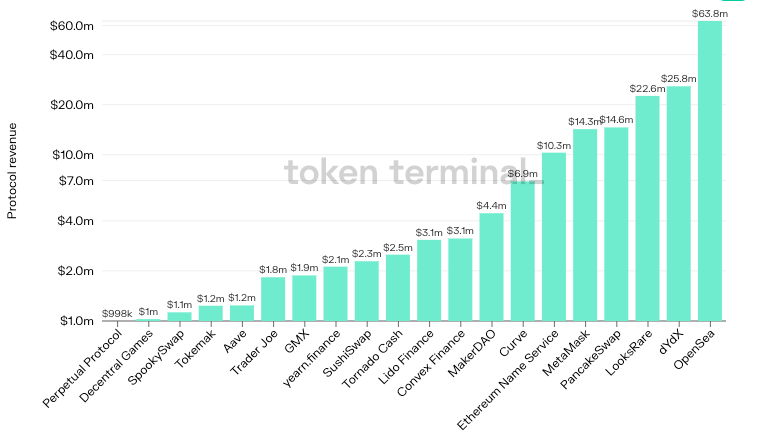
Figure 10 - Protocol gross revenue in May 2022. Source: Token Terminal
The DeFi space remains healthy, although recent market moves would have proven otherwise to the less trained eye. However, many projects are built on unsustainable Ponzinomics backed by inflationary tokens. It's important to identify projects with actual revenue sources where the majority of revenue is siphoned back to token holders. Everything revolves around incentives.
An example of an unsustainable protocol was the Anchor Protocol (ANC). Anchor was subsidising borrowing through inflationary rewards to attract further borrower demand. Rates fluctuate regularly, but there was a short period where you could get paid for borrowing. Borrowers had to pay 20%, but they also received 27% as incentivised rewards in ANC tokens. Great for borrowers, but not so much for ANC token holders. When these rewards dry up, borrowing demand and revenue plummets - as seen in the last weeks during the LUNA/UST fiasco.
The main red flag in the DeFi space is protocols that solely depend on a revenue source completely reliant on new buyers (Ponzinomics 101). Secondarily, you also want to see continual activity and shipping by developers - it’s easy to gain traction in a bull market, but can a project sustain this during a bear market when revenues are lessened?
DeFi Alpha - Our Take
We are not affiliated with any of the below projects, these are our own views. For full disclosure - we personally hold the below tokens. We maintain a realistic long-term investment horizon and have full faith in the vision of all the development teams mentioned. Data snapshots are taken on 31/05/2022 from Coinmarketcap and CoinGecko. Projects and descriptions given are non-exhaustive.
We view the rapidly growing DeFi space as a giant financial jigsaw with missing pieces constantly being added and improved to create a more robust, faster, efficient decentralised version of the current centralised financial system.
When searching for young projects/protocols that we see solving a real-world problem and capturing value in the long-term, we have found it highly beneficial to deep-dive into the development team and founders. Historically in crypto markets, teams that have only shipped products during bull markets tend to lose momentum during bear markets or prolonged market downturns. This tends to be because the team or founders lack experience. On the other hand, if the founders have been in the space for a more extended period and have a good grounding in traditional finance, the protocol tends to be more robust and development is more sustainable.
To further develop this picture, we examine the activity of the builders on https://github.com/. The GitHub repo of a given project provides an open window to look at the frequency and quantity/quality of commits. This then allows us to develop a much better understanding of the momentum and direction of the project. We have linked the whitepaper (project proposals), web page and Twitter page for each respective project below.
Frax is the world’s first fractional-algorithmic stablecoin, introducing the world to the concept of a cryptocurrency being partially backed by collateral and partially stabilised algorithmically.
Frax is interesting for a couple of reasons. Firstly, it’s another stablecoin iteration, but it’s using a genuinely novel concept by employing fractional algorithmic backing. This hasn’t been done before and in the wake of the LUNA fiasco, it’s clear that significantly more work is needed on making algorithmic stablecoins safe and effective. Frax may very well be doing that work.
Secondly, the Frax Share token (FXS). FXS is a non-stable utility token in the protocol that holds rights to governance and all system utility. Though FXS is a governance token, the Frax protocol is not managed by a DAO in the same way as MakerDAO. Governance is minimised in the extreme, with the only governance functions that the community can get involved with being adding/adjusting collateral pools, adjusting various fees (like minting or redeeming) and refreshing the rate of the collateral ratio. The goal of this approach is to allow the developers to focus on shipping the product and features they know the protocol needs, being significantly more time-efficient in the process as no time is spent upon courting the community for certain proposals. This reduces community participation on the one hand but significantly reduces politics and bureaucracy on the other.
Less red tape means greater speed of delivery and in a market where innovation exists in a perpetual state of iteration, this could be the fine line between success and failure.
Whitepaper - https://docs.frax.finance/overview
Webpage - https://frax.finance/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/fraxfinance
Directionless delta neutral yield is more important than ever in current market conditions. Basis markets are attempting to provide the DeFi ecosystem with the ability to capture inefficiencies in funding rates and spreads between spot and perpetual futures with little to no risk. As discussed briefly in the above section, this is a common strategy many hedge funds and larger asset management firms have, as discussed in the above paragraph - ‘Ponzinomics 101’.
Basis Markets provides several benefits over other strategies, such as the classic basis trade and long/short strategy across exchanges. The key features of this strategy are zero directional risk, no impermanent loss, diversified exposure, light-touch management and a longer passive return horizon.
The two main barriers to entry of such a strategy which Basis Markets are addressing are:
Alpha opacity - Many institutions utilising the strategy don’t share their data with the wider market to maintain their edge.
Perceived complexity - People are scared off from trying to implement such a strategy due to the plethora of vocabulary (contango, backwardation, delta) and would rather use vanilla trading opportunities and vehicles.
Using classic risk management in a trading portfolio, an individual rarely exposes more than 1-3% of the entire stack in any one trading opportunity. This leaves >95% of the total portfolio unproductive and in a perpetual state of dormancy. Utilising Basis Markets in the dormant portion of the portfolio could mean significantly growing with low risk due to the non-directional nature of the protocol strategy. In this manner, an unproductive stablecoin stack can be grown dramatically whilst maintaining a risk-off posture.
The $BASIS token is yield paying. The funds for payments come from the performance fees levied on all Liquidity Pool users. Anyone providing funds to the Decentralised Basis Liquidity Pool pays 24% of profits generated. All fees are paid weekly to holders. We also particularly like the tokenomics of this protocol as it incentivises and promotes decentralisation of the ownership model whilst still offering attractive rewards to token holders for participation.
With the impending launch of the Decentralised Basis Liquidity Pool (DBLP), we are keen to see this project’s progression and wager that it will become a behemoth with time.
Whitepaper - Basis Markets Overview
Webpage - basis.markets
Twitter - basis.markets (@basismarkets) / Twitter
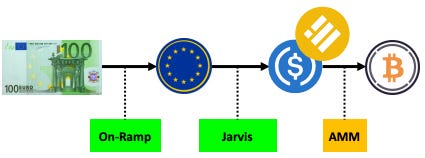
The roll-out of an efficient remittance corridor with full forex market integration is a critical hurdle in DeFi that builders and developers are tackling. Jarvis Network is making significant progress in overcoming this challenge.
Non-USD stablecoins usually struggle to maintain their peg through various liquidity issues, preventing them from attaining the network effect required to be fully usable. Jarvis Network benefits from a zero fee fiat on/off-ramp utilising the banking rails of its Swiss partner Mt Pelerin and their hosted bridge wallet.
Synthereum is the first protocol of the Jarvis Network. Synthereum's role is to solve these issues and to launch non-USD stablecoins (jFIATs), which are designed to onboard and retain users in DeFi and facilitate access to liquidity and yield. The protocol pioneers a capital-efficient way to issue and exchange fiat currencies called jFIATs, on multiple EVM-compatible networks, without price impact. jFIATs are stablecoins for decentralised and centralised finance, designed to be usable and cross-compatible - they maintain their peg at all times and are highly liquid and infinitely scalable.
jFIATs can be converted between themselves and USDC/BUSD with zero price impact on-chain and in a 1:1 ratio using live oracle price points on protocols such as Chainlink via the Mt Pelerin fiat on and off ramp. Furthermore, Curve liquidity pools such as the 3Pool or other fiat-backed stablecoin pools, can be used as a fiat on and off-ramp by proxy. This means that someone in Brazil, for example, could buy jBRL with BRL by using BRZ and swapping for jBRL.
The Jarvis Reward Token (JRT) is designed to align the interest of all the stakeholders and reward them. JRT and JRT-ETH LP tokens (together “JRTs”) can be staked, locked or delegated to benefit from rewards and key features. Eventually, an NFT-based gamification system rewarding user engagement with the protocol will be in place to further amplify stakeholder benefits.
The main sticking point is the fx fluctuation risk; however, with $8M in assets (MATIC), sensible debt ceilings per currency and the moderate nature of fx moves, the risk of loss is manageable.
We feel that if Jarvis Network achieves full scale and widespread adoption, it is currently one of the best-poised protocols for crypto onboarding with traditional finance. Jarvis Network isn’t competing with banks; it acts as a conduit for banking rails to access the blockchain.
Whitepaper - https://learn.jarvis.network/basics/mission
Webpage - https://jarvis.network/
Twitter - https://twitter.com/Jarvis_Network
QiDao is a stablecoin protocol with similar architecture to MakerDAO/DAI. Users deposit their collateral into a vault and can then borrow MAI against that collateral. The key difference is that 0% interest is charged on that loan and the user can repay it at any time. This is not the only “free money” loan platform, but it is unique in how the loans are distributed and repaid. We need multiple methodologies within DeFi to facilitate the same functions alongside protocols acting in synergy to achieve an overall full suite of DeFi products to rival the CeFi banking system.
Vaults are NFTs in their own right - therefore, the risk from each loan a user takes out is compartmentalised. If the collateral value falls below the liquidation threshold, the user will also only be partially liquidated to bring the risk ratios back into alignment. Though active risk management is still required, partial liquidation is significantly more gentle than a full equity evaporation.
The QiDao team - @0xkila, @0xLaoZi, @Wraithers_ have built a massive foundation across many different chains and built relationships/federated with many other protocols such as Balancer, Trader Joe and Beethoven X (all mentioned here).
Whitepaper - Mai Finance
Webpage - Mai.finance
Twitter - Qi Dao (@QiDaoProtocol) / Twitter
Alchemix is a self repaying loan platform, providing instant capital similar to QiDAO. Alchemix achieves this through a completely different mechanism. Users deposit their collateral into the platform and can immediately receive 50% of the collateral value back in alUSD, which can be converted to fiat through a third party and withdrawn without selling any assets. This collateral is then deployed across several DeFi protocols and the yield from that deposit is used to repay the loan and interest over time. The user can withdraw their collateral at any time and will only receive a haircut for the loan amount that remains outstanding. To add to this, loans are liquidation free. If the value of the collateral drops, the time taken to repay will increase, but the user will not be liquidated.
The team is very active on social media, with solid marketing and branding. The project is always looking to innovate with new ideas and strategies; the below is taken from their whitepaper:
“When Alchemix was originally launched, we never anticipated our peg stability module, the Transmuter, to exceed 9 figures in value, with both the alUSD and alETH transmuters holding over $100m in value each. To take advantage of this, Alchemix began deploying these reserves in Yearn and passed the extra yield from these deposits to DAI and ETH depositors in Alchemix. This enabled us to have a killer feature — boosted yield, which at times, doubled the amount of interest paid to Alchemix depositors. Recently, it dawned on the Alchemix team that these DAI and ETH reserves could be more intelligently deployed to benefit the Alchemix ecosystem. Instead of these assets passively making money elsewhere in DeFi, it makes much more sense to use these funds actively in the market to earn the protocol income and to better manage our pegs.”
The above is an excellent example of the robustness and creativity needed to maximise yield for investors, thereby repaying loans faster with locked collateral. Productivity increases with Alchemix at scale to benefit both investors and protocol alike. We are very bullish on the long term prospects for this project, given the flexibility and real-world utility it offers investors.
Whitepaper - Getting started - User docs
Webpage - Alchemix
Twitter - Alchemix (@AlchemixFi) / Twitter
Beethoven X is a protocol built on Balancer V2 and is the first next-generation AMM protocol on Fantom. Beethoven X utilises various leading DeFi protocols to offer novel decentralised investment strategies.
Beethoven X allows users to create a unique crypto index fund tailored to their desired asset allocations, enabling them to collect fees from traders who rebalance their funds through a multitude of market arbitrage opportunities. By building on Balancer V2, the most efficient trading is facilitated by pooling crowdsourced liquidity from multiple investor portfolios. Using the unique Smart Order Router, traders can find the best available price.
From our perspective, Beethoven X is interesting as it’s reimagining the well-established business model of index fund functionality. By returning fees to investors and providing traders with a plethora of potentially profitable arbitrage opportunities, the entire model of how an index fund is supposed to function is upended. This reimagining of existing structures is where the true value lies; the team from Beethoven X seem to be subscribing to the view that ‘just because something has always been done in a certain way, doesn’t necessarily mean it’s the most efficient way’.
Whitepaper - Beethoven X Overview
Webpage - Beethoven X
Twitter - Beethoven X (@beethoven_x) | Twitter
Gains Network is developing gTrade, an extremely liquidity-efficient and user-friendly decentralised leverage trading platform. The architecture used by Gains Network claims to make gTrade 100x more capital efficient than any existing platform. This allows for low trading fees, leverage up to 150x on cryptos and stocks and up to 1000x on forex with many more novel pairings in the pipeline.
The protocol revolves around an ERC20 utility token (GNS) and ERC721 utility token (NFT), actively used within the platform. We like the the trading architecture and the symbiotic ‘mint and burn’ relationship between GNS and the DAI vault. Through trading on gTrade - when a trader “wins”, new GNS is minted and when a trader “loses” the equivalent amount of GNS is burnt. As trading is a zero-sum game, this maintains supply in a state of relative equilibrium. Further, the bots executing limit orders and liquidations are powered by the Gains NFTs.
Gains is one of the few protocols in DeFi (along with others in this thread) that produces positive organic cash flow to holders. This could indicate that more mind has been paid to treasury construction and deployment, which, as previously mentioned, is a huge positive for us. Long-term, we are very excited about this project.
Whitepaper - Overview - Gains Network
Webpage - gTrade
Twitter - Gains Network 🍏 (@GainsNetwork_io) / Twitter
Trader Joe is a one-stop trading platform on Avalanche, launching first with regular trading and later with lending. These will eventually be combined to enable leveraged trading, offering a full suite of DeFi products across multiple chains.
Trader Joe being built on Avalanche offers several significant advantages over using the Ethereum blockchain. Avalanche is currently faster and cheaper. Transactions complete in around 2 seconds - the fastest of any L1 protocol. To put this into perspective, Ethereum’s completion time is approximately 6 minutes, whilst Polkadot is roughly 60 seconds. Gas fees on Avalanche are also extremely low and from experience tend to be around $0.10 - $0.20.
The team describe themselves as “degen DeFi users” focused on what they know best - DeFi. The long term goal is to make Trader Joe an R&D-focused platform for new DeFi offerings not yet seen on any blockchain and though they first deployed on Avalanche, their vision expands much further. This is a crucial point as the team will be actively seeking to drive innovation via the platform, providing novel revenue streams for the protocol and returns for investors. Any team looking to build on predecessors and provide novel offerings fulfil our criteria for potential investment.
The platform doesn’t follow the same UI format as other DEX’s and is clean and easy to navigate. The platform offers a DEX with a handy candlestick chart and another cool feature: the zap feature. If you find that you want to pair JOE with AVAX as an LP and farm it, you can hit the zap tab and select what crypto you would like to convert to the JOE-AVAX LP and hit zap. Instead of having to convert to both JOE/AVAX and then approve JOE, approve AVAX and then finally hit add liquidity, you can bypass these unnecessary steps using zap and head straight to the LP token, saving you gas fees as well.
JOE comes with a dual staking mechanism that generates double yield. If you have used Sushi Swap, you will be familiar with xTokens. Trader Joe has a similar process with their single-sided JOE staking, thereby mitigating the issue of impermanent loss.
The team has a solid background in both crypto and more traditional tech roles, which will likely translate well into the tenacity needed to succeed in the long run and actually deliver on rollout promises/proposals. They’ve also nailed the marketing, which is often an afterthought in the crypto space.
Whitepaper - Trader Joe
Webpage - Trader Joe
Twitter - https://twitter.com/traderjoe_xyz
Balancer is a protocol with multiple facets, leveraging a community-driven approach, automated portfolio manager, liquidity provider and a price sensor. These combine to deliver a decentralised exchange and automated portfolio management of tokens on Ethereum and other EVM compatible systems. Balancer enables decentralised swaps and liquidity provision and features to reduce gas costs, improve capital efficiency, unlock arbitrage with zero-token starting capital and open the door to custom AMMs.
Balancer pools with high token counts act like index funds, allowing users to have access to broad exposure to a variety of tokens. Where Balancer differs from the traditional notion of an index fund is in the fees. Instead of paying broker fees to rebalance the pool, the pools collect the fees as they are continuously rebalanced by traders making swaps. High token-count pools have many token pairs, creating additional opportunities to collect trading fees and more trading opportunities.
In essence, liquidity providers collect trading fees while enjoying continuous rebalancing of their portfolio whilst traders gain access to an open, decentralised exchange, with no downtime and minimal fees.
Whitepaper - Balancer Overview
Webpage - Balancer
Twitter - Balancer Labs (@BalancerLabs) / Twitter
Curve is one of the dominant protocols in the DeFi arena - providing the muscle to many other composable DeFi projects offering yield through the Curve ecosystem. As the dominant decentralised liquidity aggregator, anyone can add their assets to several different liquidity pools and earn a share of the fees.
This may not sound particularly novel; however, a unique pricing formula in the stablecoin swapping mechanism and deep liquidity means that Curve can compete on slippage with centralised exchanges and OTC desks for even the largest swaps. Furthermore, Curve is incredibly efficient at swapping between stablecoins and tokenised versions of blue-chip assets, such as WBTC, renBTC and sBTC. Curve also benefits from first mover advantage, capitalising on these ideas very early in the DeFi revolution and doing so with extreme simplicity with its nostalgic windows 98 UI/UX. Raw functionality is what we get, not frilly marketing and graphics.
CRV currently trades with a Market Cap / TVL Ratio of 0.06. If yield farming, you'll want to dynamically adjust your allocation to both stable coin farming and blue-chip token farming, depending on the supply/demand outlook. Platforms like CRV offer counter-cyclical opportunities but remember to keep a sensible level of portfolio exposure and continually recycle profits.
Whitepapers - Curve DAO + Automatic market-making with dynamic peg + StableSwap - efficient mechanism for Stablecoin liquidity
Webpage - Curve.fi
Twitter - Curve Finance (@CurveFinance) / Twitter
Oracle Services Previously Mentioned
Chainlink is a decentralised oracle provider. One of the major criticisms of blockchain and smart contracts is the lack of real-world connection or use cases. Chainlink fixes these issues by enabling smart contracts on any blockchain to connect with and leverage extensive off-chain resources, such as tamper-proof price data, verifiable randomness, keeper functions and external APIs.
Whitepaper - Chainlink 2.0 Whitepaper
Webpage - Chainlink
Twitter - Chainlink
Witnet is a reputation-based decentralised oracle network aiming to combat some of the aforementioned attack vectors. Nodes running Witnet earn or lose reputation when they correctly or incorrectly fulfil a data request, where correctness is defined by a consensus algorithm analysing nodes’ answers. Nodes which disagree with the consensus lose reputation (by being off-line or attempting to be malicious), which is split between honest nodes. If the consensus was a timeout, as long as a node agrees with the consensus, it remains unpunished. In this way, Witnet is offering a scalable solution with reduced on-chain operational fees.
Whitepaper - witnet-whitepaper.pdf
Webpage - Witnet
Twitter - Witnet $WIT — The Multichain Decentralized Oracle (@witnet_io) / Twitter